Seawater desalination is a critical method for augmenting water supplies worldwide. Every day, numerous desalination plants convert seawater into drinking water, producing millions of cubic meters of fresh water to support domestic, agricultural, and industrial needs. This article examines the daily output of desalinated water, evaluates the efficiency of desalination processes, and discusses their regional applications.
Daily Production of Desalinated Water
Currently, there are about 16,500 seawater desalination plants operating in 185 countries globally. These plants collectively produce around 110 million cubic meters of fresh water each day. This substantial production underscores the vital role of desalination in providing a reliable freshwater source.
In the United States, small desalination units are often found near natural gas and hydraulic fracturing sites, supplying necessary water resources for these industries. The presence of these units highlights the importance of desalination in supporting industrial activities that require significant water resources.
Achieving High Production with Advanced Technology

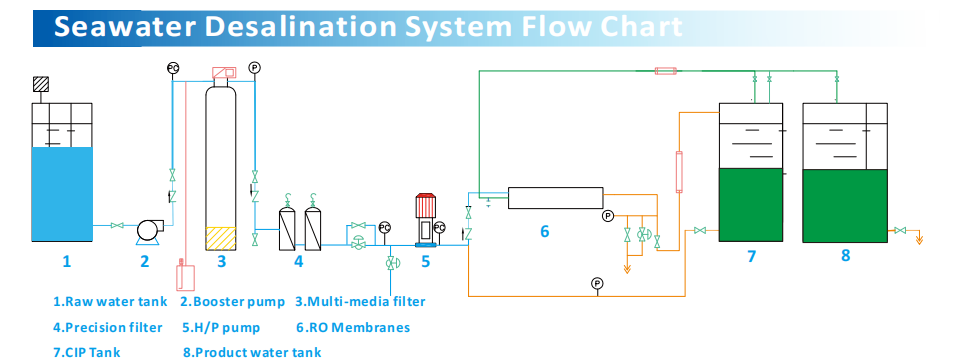
The significant daily output of fresh water from desalination plants is made possible by advanced technologies and efficient operational processes. Most desalination plants use reverse osmosis (RO) technology, where seawater is forced through a semipermeable membrane by high pressure, separating salt and other impurities. Additionally, these plants utilize sophisticated pre-treatment systems, energy recovery devices, and comprehensive control systems to ensure stable and efficient operations.
Key Factors Influencing Efficiency:
- Energy Consumption: Desalination processes, especially RO and distillation, require substantial energy. Enhancing energy efficiency is crucial to improving overall operational efficiency.
- Membrane Technology: Advances in membrane technology, including RO and nanofiltration, have significantly boosted desalination efficiency by increasing water throughput and reducing energy consumption.
- Water Quality Management: Customizing pre-treatment and desalination methods to match the specific characteristics of the input seawater helps optimize efficiency by reducing energy use and maximizing output.
Regional Applications of Desalination Plants
The deployment of desalination plants varies significantly by region, influenced by local water scarcity, economic conditions, and technological capabilities.
- Middle East: The Middle East, particularly Saudi Arabia, relies heavily on desalination due to its arid climate and limited freshwater resources. This region hosts some of the world’s largest desalination plants, essential for meeting domestic water needs.
- Australia and the United States: In these regions, desalination plants play a key role in urban water supply and agricultural irrigation. Both countries have made significant advancements in desalination technology, improving its efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
- Developing Countries: In many developing nations, the adoption of desalination technology is limited by cost and technical barriers. However, international collaboration and technology transfer are gradually facilitating the deployment of desalination solutions in these areas.
Desalination is a crucial technology for addressing global water shortages, with ongoing advancements promising even greater efficiency and broader application.
